概要
Spring MVC 是建立在IoC容器的基础之上的。了解Spring MVC,首先要了解Spring IoC容器是如何在Web环境中被载入,并起作用的
Spring IoC是一个独立的模块,它并不是直接在Web容器中发挥作用的,如果在Web环境中使用IoC容器,需要为IoC设计一个启动过程,将IoC容器载入,并在
Web.xml配置 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
<servlet >
<servlet-name > mvc</servlet-name >
<servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class >
<init-param >
<param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name >
<param-value > classpath:spring/spring-mvc.xml</param-value >
</init-param >
<load-on-startup > 1</load-on-startup >
<async-supported > true</async-supported >
</servlet >
<servlet-mapping >
<servlet-name > mvc</servlet-name >
<url-pattern > /</url-pattern >
</servlet-mapping >
<context-param >
<param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name >
<param-value > classpath:spring/spring-dao.xml,classpath:spring/spring-service.xml</param-value >
</context-param >
<listener >
<listener-class > org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class >
</listener >
在上面的配置中,首先定义了一个Servlet,它是Spring MVC 的DispatcherServlet,在Spring MVC中是一个很重要的类,起着分发请求的作用,同时
IoC容器在Web环境中的启动过程 IoC容器启动的基本过程 IoC容器的启动过程就是建立上下文的过程,该上下文与ServletContext相伴而生的,同时也是IoC容器在Web环境中的具体表现之一。由ContextLoaderListener启动的
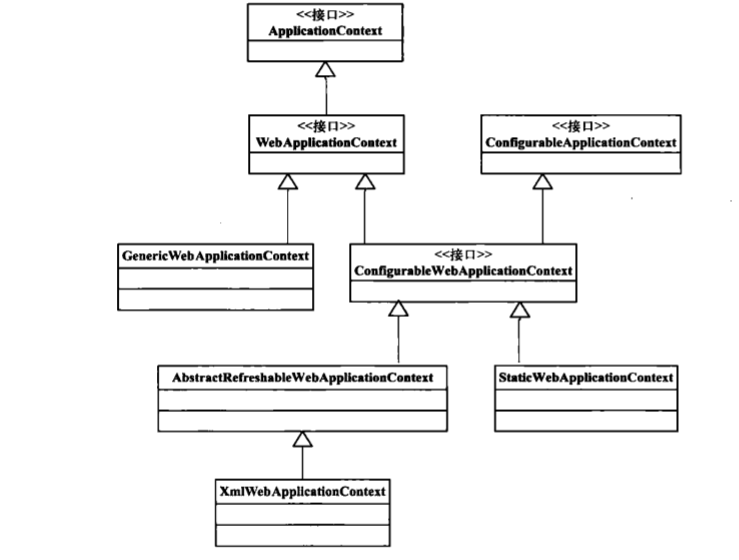
WebApplicationContext接口的继承关系
在这个类继承关系中 , 可以从熟悉的XmlWebAPPlicationContext入手来了解它的接口实现.在接口设计中 , 最后是通过ApplicationContex接口与BeanFactory接口对接的 ,
在启动过程中,Spring会使用一个默认的WebApplicationContext的实现作为IoC容器就是XmlApplicationContext,在继承了基本的ApplicationContext功能的基础XmlApplicationContext的初始化过程中,Web容器中的IoC容器被建立起来,从而在Web容器中建立起整个Spring应用BeanDefinition一样,只不过多了一些读取指定配置文件的applicationContext.xml文件的细节。
为了了解IoC容器在Web容器中的启动原理 , 这里对启动器ContextLoaderListener的实现 进行分析. 这个监听器是启动根IoC容器并把它载入到Web容器的主要 ,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext (ServletContext servletContext)
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null ) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!" );
} else {
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext" );
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started" );
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
if (this .context == null ) {
this .context = this .createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this .context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)this .context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null ) {
ApplicationContext parent = this .loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
this .configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this .context);
}
}
创建WebApplicationContext的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext (ServletContext sc)
Class<?> contextClass = this .determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]" );
} else {
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
}
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter("contextClass" );
if (contextClassName != null ) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var4) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]" , var4);
}
} else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var5) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]" , var5);
}
}
}